| Notable
Features |
| . |
 |
Reuse
of the existing building structure, avoiding total demolition
of the building and minimizing the generation of demolition waste. |
 |
Rehabilitation
of industrial building, and therefore revitalization of the district. |
| . |
 |
| . |
| Basic
Information |
| . |
 |
Location:
Situated on the south side of the River Thames, opposite St Paul's Cathedral. |
 |
Architects:
Herzog & de Meuron, Jacques Herzog, Pierre de Meuron, Harry Gugger and
Christine Binswanger. |
 |
Construction
Manager: Schal, a division of Carillion plc. |
 |
Conservation
cost: 134 million pounds. |
 |
Date of original
building construction: Built in two phases, 1947 and 1963. |
 |
Project and
construction date: 1995/2000. |
 |
Architect of
origin: Sir Giles Gilbert Scott. |
 |
Site Area: 3.43
Ha |
 |
Total floor
area: 34,500 m2 including: |
| - |
Gallery suites
for display and exhibition of 7,827 m2. |
| - |
The former
turbine hall as a "covered street" of 3,300 m2,
where works of art may be shown. |
| - |
A special
exhibition suite of 1,300 m2. |
| - |
A 240 seats
auditorium. |
| - |
2 cafes. |
| - |
3 shops of 500,
300 and 150 m2. |
| - |
An educational
area of 390 m2. |
| - |
A member room of
150 m2. |
| - |
1,350 m2
of offices. |
| - |
A support
services/art handling area of 1,500 m2. |
| - |
9 passenger
lifts of which 4 are for public use. |
| - |
6 escalators. |
|
.
|
|

|
| . |
| History
of the Building |
| . |
|
Sir
Giles Gilbert Scott designed the original bank power station. The building was
built in two phases between 1947 and 1963. The western half of the structure,
which included the chimney, replaced an earlier coal-fired power station, in
1952. The eastern half of the building was brought into commission in 1963. In
1981, the bankside power station closed. Between 1981 and 1994 the building
remained unoccupied apart from an operational London Electricity sub-station
that still remains.
|
|
.
|

|
|
.
|
| Description
of the Building |
| . |
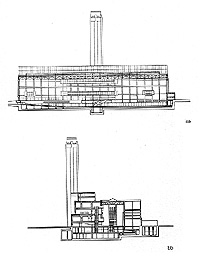
| The
building consists of a brick-clad steel structure, constructed from more than
4.2 million bricks. The height of the central chimney was limited to 99 m (in
order to be lower than the dome of St Paul’s Cathedral), and the northern
frontage of the building is over 200 m long.
|
| . |
 |
|
|
![]() |
|
| Overview
of the new Building |
| . |
|
The architect team,
Herzog & de Meuron, have respected the integrity of the original design of
the building, keeping the existing structure and adding bridges, balconies,
new floors and wall systems and a two-storey glass structure and light beam
spanning the length of the roof. The architects strategy was to accept the
physical power of Bankside’s massive mountain-like brick building and to
even enhance it rather than breaking it or trying to diminish it. New volumes
and surfaces have been created to fit in with the new function of the building
avoiding major demolition of the building structure. A dialogue has been
created between old and new architecture and materials enhancing the image of
the building.
The
transformation of the building began in 1995 with the removal of all the power
station machinery. Other works included the removal of the roofs of both the
old Boiler House and the Turbine Hall, the demolition of a number of out
buildings and sandblasting and repainting of the remaining steelwork. Work on
the first piece of construction, a vast concrete raft, forming a foundation on
which the museum sits, commenced during October 1997. This was followed by the
fabrication of the structural steel framework in the former boiler house,
creating the seven floors and effectively forming a new building within the
walls of the old. This was followed by the creation of the seven gallery
floors. During this process the original boiler house trusses were removed,
allowing the new floors to fully support the existing brick façade. In May
1998, the steelwork for the new two-storey glass roof structure began, and in
autumn the roof of the turbine hall was replaced allowed fitting out to
commence. The construction ended in January 2000, and Tate Modern opened to
the public on 12 May 2000. |
 |
| . |
| References |
| . |
|
|
| . |
 |
| . |
| Site
Plan |
| . |
|
| . |
 |
| . |
| Sections |
| . |
|
| . |
 |
| . |
| External
view with extension |
| . |

|
| . |
 |
|



