|
|
| Notable Features | |
|
|
Wastage level and targets |
|
|
Prefabricated bathroom modules |
|
|
Precast cladding panels |
|
|
Prefabricated stair and lifts |
|
|
Prefabricated roof panels |
|
|
Adaptability |
| Basic Information | |
| Location: | |
|
Southern end of Greenwich peninsula site, London, UK |
|
| Building Type : | |
| Residential, and mixed | |
| Contract Period: | |
|
Construction of phase 1 started in December 1999-Phases over a five-year period |
|
| Contract Sum : | |
| Approximately £250 million | |
| Site Area : | |
| 13 hectares (32.3 acres)? | |
| Gross Floor Area : | |
| Typical Floor Area : | |
| Client : | |
| Greenwich Millennium Village Ltd, a joint venture development between Countryside Properties Plc and Taylor Woodrow Plc. | |
| Housing associations : | |
| Moat Housing Association, Ujima Housing Association | |
| Architect : | |
| Ralph Erskine (master plan) with the support of EPR Architects (phase 1), Proctor Matthews Architects (phase 2). | |
| Landscape architects: | |
| Randle Siddley Associates, Robert Rummy Associates | |
| Planning consultant: | |
| Montagu Evans | |
| Innovation consultant: | |
| Richard Hodkinson | |
| Cost consultant : | |
| WT Partnership | |
| Environmental engineer: | |
| Taywood Engineering | |
| Structural engineer: | |
| Waterman Partnership, Thorburn Colquhoun | |
| Services engineers: | |
| WSP, Thorburn Colquhoun | |
| Quantity surveyor: | |
| Main contractor: | |
|
|
|
| . | |
| Overview | |
| The Greenwich Millennium Village is part of the Greenwich Peninsula Development which includes the Millennium Dome, 3,000 homes, 50 acres (20 hectares) of parkland, an ecological park, a commercial area and transport links. | |
|
This residential development including 1377 homes (298 houses and 1079 apartments), ranging from one-bedroom apartments to penthouses, is designed to set national standards for future developments, minimizing environmental impacts and maximizing sustainability. The development also includes a community center, a primary school, a health center, shops, cafes, bars, and offices. |
|
|
The first phase of the development comprises 100 apartments at the northernmost part of the site beside the Thames and a new lake. The second phase comprises a mixture of two-or-three storey houses with gardens, arranged in ribbon fashion, together with 1,2, and 3 bedroom apartments arranged around the garden squares Factory produced modules: bathrooms, cladding panels, plant rooms, services risers, stairs and lifts. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Prefabricated Bathrooms Units | |
| The units were delivered as complete rooms fully fitted to include all services that are pre-commissioned. The units were standardized in size and configuration although some flexibility in final specification was available to meet consumer selections. The units were made from structural steel framing to which were fixed lightweight metal supports for plasterboard. | |
|
|
|
| Precast Staircases | |
| Precast concrete stairs give early safe access to work areas. | |
|
|
|
| Wastage Level and Targets |
| Source: http://greenwich-village.co.uk |
|
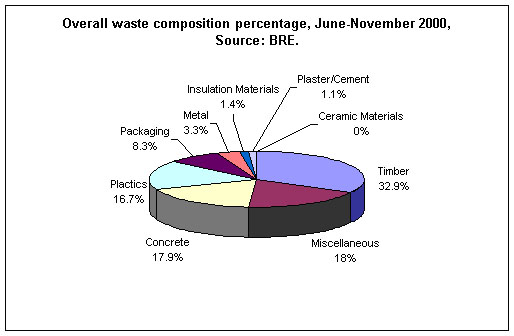
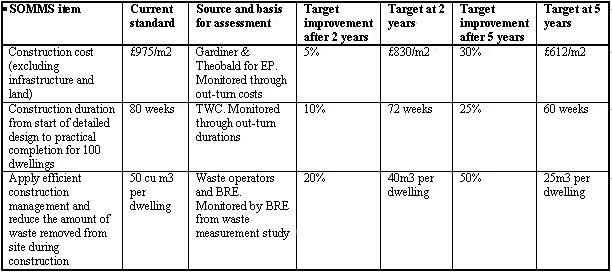
With 40% of UK waste arising from construction an important concern is to reduce the amount of waste arising from construction sites. Measurements of skip volumes removed from sites showed typically 50m3 of construction waste per dwelling. There was a continuous waste audit. One of the targets was to reduce construction waste generation by 50%. |
|
Improvement
benchmarks table (source: http://greenwich-village.co.uk) |
|
|
|
|
| Cladding Panels |
|
Cladding panels were factory made to provide early weather tightness to the building to allow early internal fit out. The panels were 1-storey height and 6m long. The panels were made in two parts (source: http://greenwich-village.co.uk): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Prefabricated Roof Panels |
|
Complete factory made roof panels with roof drainage outlets built in. These provided early weather tightness of the building together with the cladding panels. |
|
|
| Adaptability |
| “Buildings need to change to meet the changing needs of their occupiers”. The adaptability concepts provides long life span of the building structure and therefore avoid demolition of the whole building. Several design solutions were reviewed to give greater levels of adaptability such as: |
|
|
|
|
|
Web site: http://greenwich-village.co.uk |
|
|